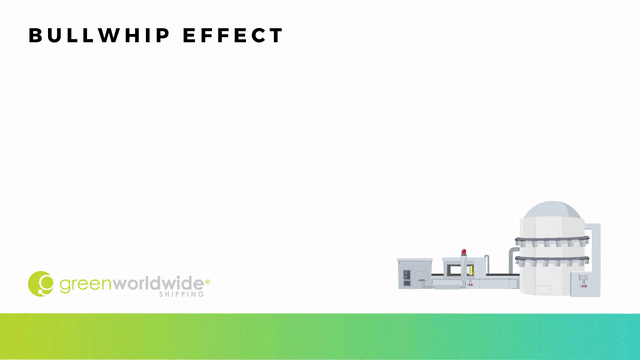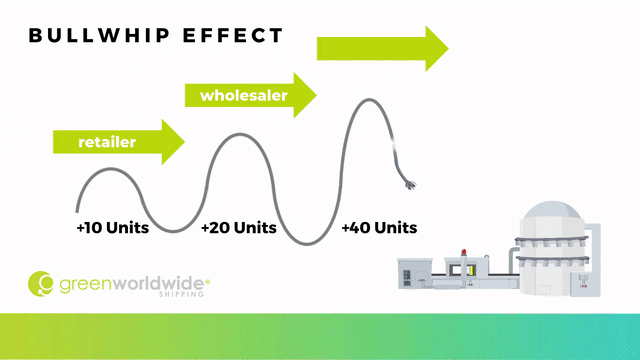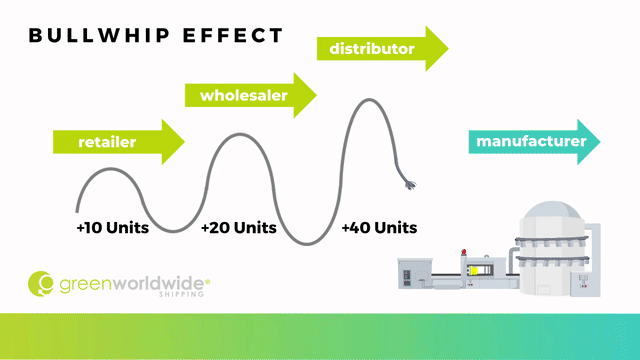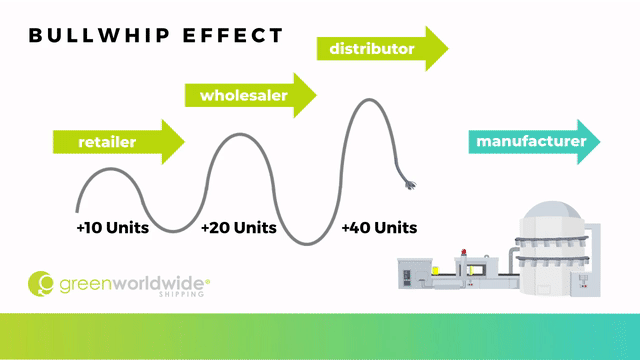
The term “bullwhip effect,” first introduced by Jay Forrester and is also known as the Forrester effect, refers to a type of demand distortion caused by incorrect forecasting that leads to progressively larger fluctuations in materials orders going upstream in the supply chain from the retailer to the wholesaler, distributor and all the way to manufacturing.
When a consumer places an order, the purchase is perceived as a demand increase, cracking the whip, and sending a signal that is amplified in forecasts of each layer of the supply chain. There are 5 main factors that contribute to the bullwhip effect: demand signaling, lead time, order batching, price fluctuation, and shorting. The greater the supply chain, the greater the potential distortion for upstream partners.
Now, shippers with trans-Pacific supply chains are concerned that COVID-19 related factory lockdowns in Asia will lead to a bullwhip effect, due to increased lead times and delayed inventories. Businesses that have lost weeks of production are now realizing how important it is to diversify their supply chains.
EXAMPLE BULLWHIP
For example, if a gardening store with an inventory of 25 gloves normally sells five a day, it would usually order that replacement amount from the wholesaler to ensure its inventory was maintained. If, however, one day the store sells 10 gloves and believes that customers will continue to buy more and more of the item, it may respond by ordering 20 gloves to keep up with the new forecasted demand.
The wholesaler may then decide to order 40 gloves from the distributor as a response to the presumed higher demand, to give themselves a safety net. Finally, the distributor would also react to the change by requesting 80 additional units from the manufactures. At this point, the over-ordering has increased rapidly which can result in loss of profit.
The bullwhip effect can also work in the opposite direction as well, like when retailers misjudge how popular a specific toy will be during the holiday season and end up with a shortage.
SUPPLY CHAIN IMPACT
The bullwhip effect can be damaging to all supply chain partners. Surplus inventory can lead to waste and profit loss, whereas insufficient inventory can result in shorter lead times, poor customer experiences, and reduced business.
WAYS TO MITIGATE THE EFFECTS
- Improved communication among supply chain partners.
- Superior forecasting methods.
- Better supply chain management through visibility tools & technology.
Do you think the bullwhip effect is impacting supply chains today? Tell us how.
Need upstream visibility from Purchase Order inception to final delivery and all the data in between?
Read more about Green Engineered Management at greenworldwide.com





